The True Story Behind "The King's Speech"
"The King's Speech" is a 2010 dramatic biographical film, recounting the friendship between King George VI of England and his Australian speech therapist, Lionel Logue. The film also covers Edward VIII's 1936 abdication, and George VI's subsequent coronation and shouldering of responsibility during World War II. George VI ultimately must conquer his stammer to assist and guide Britain during the war.
As a film, "The King's Speech" takes a few liberties with the historical timeline and in regards to simplifying certain characters. One element historians took particular umbrage with was the depiction of Winston Churchill. However, overall it is fairly faithful to the historical record. For one thing, George VI really did have a speech impediment since the age of eight, and Lionel Logue did work with him for several years. They did stay friends until they both died. Certain scenes, such as George VI's coronation, were praised for their accurate recapturing of the feel of the 1930s.
The main concept the film changed was simply adding drama to certain scenes, such as the speech announcing war with Germany towards the end. It also condensed the historical timeline significantly, shortening events. This was mostly done for the sake of keeping the narrative moving. Overall, however, "The King's Speech" is a fairly accurate, heartwarming rendering of George VI and Lionel Logue's friendship.
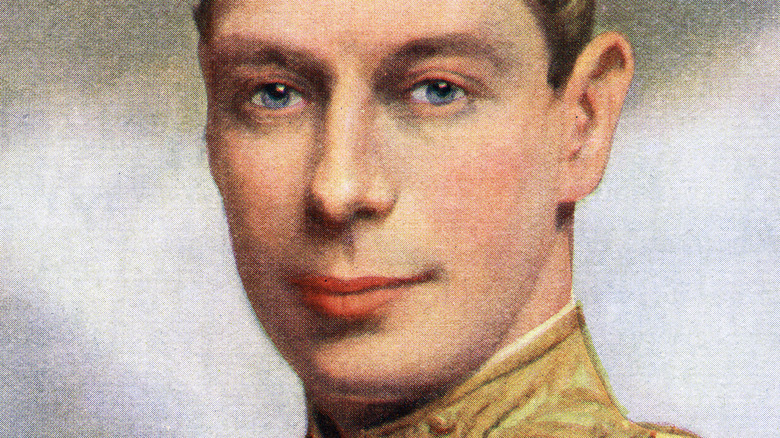
Prince Albert had a stutter as a child
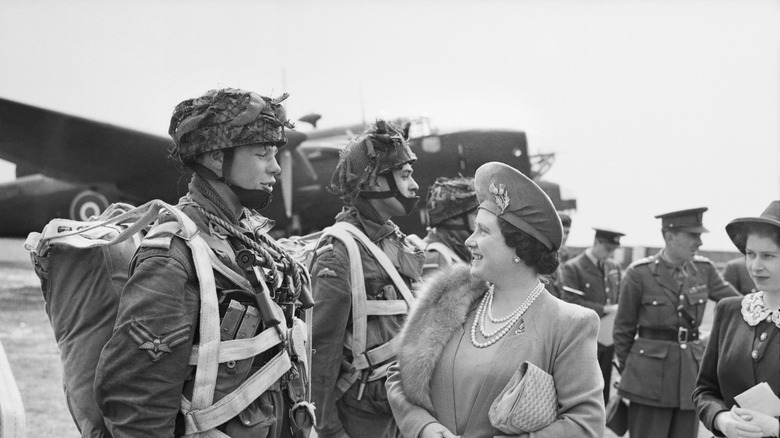
Prince Albert, later George VI, developed a stutter when he was eight that he carried through to his early adult life. His parents were not terribly affectionate with him, and he was susceptible to tears and tantrums – traits he also carried through his adult years, writes Biography. Given that many of his public duties required speeches, Albert needed to – and worked tirelessly – to fix his stammer with multiple doctors and therapists, writes Stuttering Help. He wasn't successful with any speech therapies until he worked with elocutionist and informal speech therapist Lionel Logue, beginning in the 1920s.
When Logue saw the then-Duke of York give a speech, he said to his son, "He's too old for me to manage a complete cure. But I could very nearly do it. I'm sure of that." (via Stuttering Help). He was right, and his positive attitude helped the duke recover from previous failures that had made him believe the problem caused him to be mentally deficient instead of simply physically injured. Despite how long they worked together, the duke's speech issues had more to do with how held his jaw and pronounced words; the result was that his stammer was mainly cleared up in a matter of months as opposed to years.
Lionel Logue was a self-taught speech therapist
Lionel Logue was an Australian speech therapist who, not being formally trained, used methods he had discovered and created on his own. He worked as an elocutionist first, but fell into helping Australian World War I veterans with speech defects, writes The ASHA Leader. No one else was doing what he was with the veterans, and speech therapy and audiology programs didn't even get off the ground until the 1940s (via UNC Health Sciences Library). Logue was even a founder of the College of Speech Therapists.
Just before World War I, Logue worked a variety of jobs as a teacher of elocution and drama, theater manager, and reciter of Shakespeare and Dickens (via Speech Language Therapy's Caroline Bowen, a speech language pathologist). Logue worked with patients on their speech, but also on confidence and the self-belief that they could accomplish what they set out to do. He was empathetic with his patients, and learned from each case he worked on. Logue originally tried out as an actor, and as a result, his manner was somewhere between a teacher and an artist. He was serious about his life's work and resolved to avoid cheapening it by writing a book about his efforts with the king.
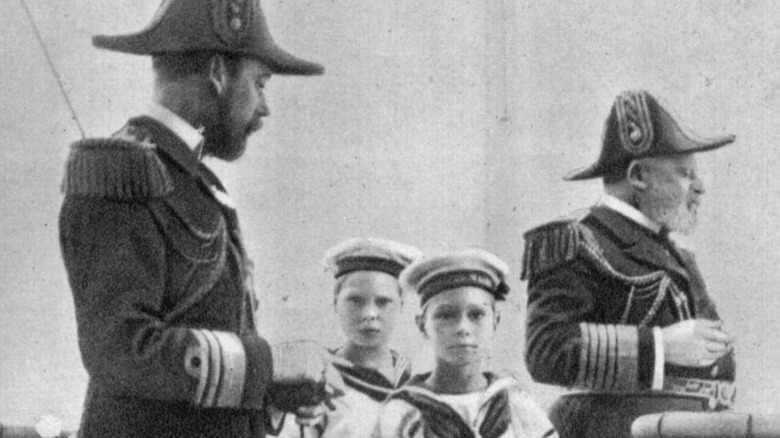
Logue began working with Prince Albert in 1926
Elizabeth, the Duchess of York, first encouraged her husband to work with Lionel Logue, though the meeting as depicted in the film between Elizabeth and Logue likely didn't happen (via Logue and Conradi's "The King's Speech"). Logue thus began working with the Duke of York in October 1926, soon after he opened his London practice on Harley Street. Logue first diagnosed the Duke with, according to CNN, acute nervous tension and the habit of closing the throat, which caused him to clip words out.
Logue met with him daily for the next two or three months (in advance of a visit to Australia), and his stammer was gone (for the most part) within that time frame; it didn't take years of treatment (via Speech Language Therapy). Unlike in the film, in reality, the Duke and Logue weren't necessarily aiming for complete fluency. However, they did continue to work together for the next two decades, mainly on the royal's speeches.
Logue worked with Albert for over 15 years
Though the film condenses the timeline to make it seem as though everything takes place over just a few years, Logue and Albert worked together for decades (via CNN). "The King's Speech" begins in 1925 with the close of the British Empire Exhibition, which would be historically accurate, but time simply speeds by until the film depicts the abdication of Edward VIII in 1936 and later the outbreak of war in 1939 in just a few hours; it doesn't really feel as though a decade and a half have passed.
Regardless, Logue and the duke worked together on speeches even after the duke had mostly mastered his stammer. Lionel Logue's methods were unorthodox and primarily self-taught. He never specifically said what course of treatment he worked on with the duke, saying, according to The ASHA Leader: "...on the matter of Speech Defects, when so much depends on the temperament and individuality, a case can always be produced that can prove you are wrong. That is why I won't write a book." Much of the ideas for the therapy sessions depicted in the film come from Logue's diaries (though plenty of the dialogue was invented), which were inherited by his grandson Mark. They were used in the film, though the director only saw them late in the film's production.
Any sort of therapy is inherently individual, not to mention personal (via Psychiatric Times). It's no wonder that Logue decided to avoid writing about his work.
Wallis Simpson was a more complex person than the film indicates
King Edward VIII was crowned in January 1936 and abdicated in December of the same year in order to marry Wallis Simpson, who had been twice divorced (via History). His younger brother was proclaimed king the next day. The film is sympathetic to George VI and Elizabeth, and Wallis Simpson is cast as a vaguely Nazi-supporting villain; there is little depth to her character. However, her life and motivations were shrouded in rumors from the British upper classes and the media.
The upper classes, who learned about the Edward-Wallis romance before the British media, in particular saw her as an uncouth American divorcee, and had a hard time figuring out why Edward wanted to be with her. When the media did find out, in December 1936, she was both ruined and revered by them, according to History Extra. However, after moving overseas more-or-less permanently she faded from the spotlight. Her unfortunate reputation from the nobles stuck with her.
Ultimately, George VI didn't allow his brother and sister-in-law, who had moved to France, to be productive for the royal family; they asked multiple times for jobs and were denied (via History Extra). Awful rumors followed Wallis Simpson even past her death in the 1980s, including one that stated she would do anything to become queen of England. Though it's clear both on and off screen that she and Elizabeth disliked each other, Wallis was more than a king-stealing villain.
Churchill was actually opposed to Edward VIII's abdication
One major element of the film that historians had trouble with is Churchill's abrupt support of George VI, writes Daily History. In real life, he encouraged Edward VIII not to abdicate in 1936, and remained a supporter of the royal, believing something could be worked out without having to resort to abdication. George VI and Elizabeth didn't fully support Churchill later in life due to his actions during the abdication. However, Churchill was later knighted by Elizabeth II (via Biography).
This element is likely written as such for the film due to the writers having a hard time writing someone as beloved as Churchill with actual flaws. The writers of "Saving Mr. Banks" had a similar issue with Walt Disney and his flaws. As a result, it is one of the only concrete historical aspects that left historians scratching their heads in confusion. Everything else that is changed in the film is mainly done for the sake of adaptation, drama, and the good of the narrative. This change seems to be for the sake of preserving Churchill's reputation. Considering the film's lead-up of events to World War II, and Churchill's role in Britain's survival, it isn't that surprising.
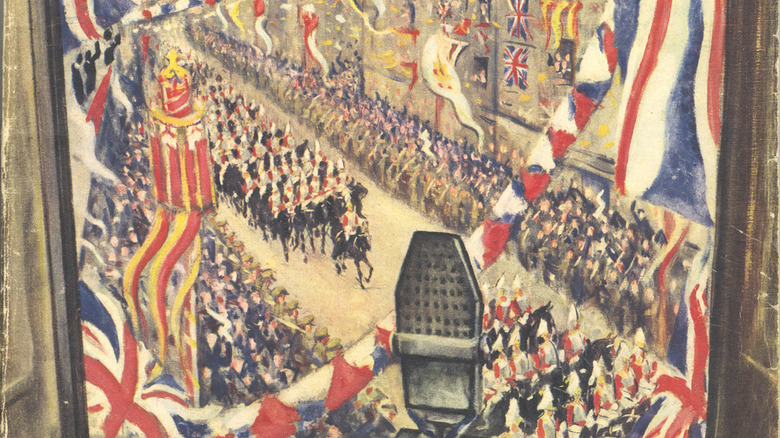
King George VI's coronation was less fraught than the film depicts
Logue worked with George VI on his coronation speech in 1937. Five days afterward, the king wrote a heartfelt thank you letter for the assistance (via Tatler), attributing the success to Logue's "expert supervision and unfailing patience." Just as in the film, Logue and his wife are seated in the royal box, so high up that Myrtle Logue needed to use opera glasses in order to see, writes CNN.
However, by this time, the king had mostly mastered his speech impediment, and the dramatic scene in the film with Logue and St. Edward's chair is likely fictional. It was written for the sake of the narrative of George VI realizing he does have a voice. Reality isn't necessarily so cinematic, and after weeks of working on the speech with Logue, George VI delivered it flawlessly. Regardless, according to Daily History, the film accurately conveys the atmosphere of the 1930s and the coronation of a new king. In reality, the king and Logue likely didn't have the same miscommunication as they do in the film, and it is doubly heartwarming that Logue and his wife were seated with the royal family, just because of the services Logue had rendered the new king.
Logue was more deferential to his royal patient
Geoffrey Rush's portrayal is much more animated than Logue likely was in reality. Logue certainly addressed Prince Albert respectfully, and the scenes of swearing in Logue's office are likely invented. Logue also never referred to the prince by a nickname, much less one used exclusively by the family. They were friends in real life, but their relationship was more realistically distant.
According to CNN, the letters Logue wrote to the king are addressed to "Your Royal Highness". On the other hand, the king signed his letters with his first name, indicating a measure of friendship between the two men. Logue also apparently allowed George VI to set treatment goals due to his position. Though they did end up being friends, Logue never forgot who exactly his patient was, and treated him accordingly (via Daily History). Historical films always add heart-to-heart speeches between people which probably never actually happened but work for the sake of drama and the narrative. "The King's Speech" is no exception.
The speech announcing war with Germany was less dramatic
Lionel Logue further assisted George VI during the 1939 speech when he announced Britain was at war with Germany. However, Logue wasn't actually in the room with him, as the film depicts, and only wrote notes on places for the king to pause to collect himself when speaking or on which words to stress, according to CNN. Keep in mind that by this point in time, 13 years after meeting Logue, the king had essentially mastered his stammer. George VI also stood to give the speech, though photographs show him in full military uniform and sitting down.
Lionel Logue's diaries also answered a previously unknown question about the speech that was added to the film. George VI stammered on some of the W's in the speech, and according to a comment he made to Logue, it was so the people would recognize him, writes CNN.
The film turns the event into a climactic event, as a culmination of the years of work the king and Logue have put into his affliction – and which the audience has just watched on screen for the past two hours. Also, though it is unlikely the information was revealed at this exact time in real life, the character of Winston Churchill tells the king just before this speech that he, too, was a stammerer as a child, writes The Lancet. This element is true, though it is positioned for the sake of cinematic drama.
George and Logue's friendship didn't fracture over credentials
In the film, coronation preparations pause when the archbishop of Canterbury, Cosmo Lang, mentions that Logue doesn't have any formal training. Not having known this beforehand, George VI becomes outraged and only calms after Logue provokes him into speaking without stammering, causing him to realize that he actually can speak accurately. This entire element is invented for the film, presumably for the sake of drama (and humor).
By this point, the two men had known each other for over a decade and were friends. Though their relationship was primarily professional, in scouting out Logue's help, the king must have understood his credentials and it didn't bother him; after all, he worked with Logue, voluntarily, for decades (via Daily History). Logue's formality likely kept their friendship professional enough that they probably had few personal disagreements.
Logue and the king wrote letters back and forth for years; the earlier letters were signed "Albert" and the later letters "George" by the king, according to CNN, indicating a measure of friendship that was likely meted out to few people. When Logue asked the king in 1948 if he would serve as patron of the College of Speech Therapists, George VI immediately agreed and it became known as the Royal College of Speech Therapy, writes The ASHA Leader.
The film has an obvious pro-George VI bias
Due to being written from a historical perspective, "The King's Speech" supports George VI, Logue, Elizabeth, and even Winston Churchill as characters and historical figures much more than it does George V, Edward VIII, or Wallis Simpson. The film has an agenda and a narrative it set out to tell: the story of how George VI overcame his stammer and led a nation successfully through a war.
According to The Gazette, the film's textual inclusion of Logue's appointment as a Member of the Royal Victorian Order is accurate. The king appreciated his services enough to reward him with a title for them, and this element certainly adds to the theme of friendship the film is so fond of.
In another interesting example of bias, however, the film omits Edward VIII's Nazi sympathies entirely, though Simpson is written to seem like an outsider to the royals. This was likely done for the sake of Edward's surviving family, though it was a slightly odd omission considering the context of the film. Edward isn't cast as a villain, however, he doesn't quite seem to realize what he's forcing his brother to step into. Though he immediately supports George, Edward doesn't seem to comprehend the royal family's – and the film's – endless demand of duty.