Why Immortality Is Closer Than You Think
We may receive a commission on purchases made from links.
Dreams of human immortality have been percolating since the dawn of humanity. Rather than relying on the possibilities of alchemy, spirituality, or religion, modern scientists have made it a mission to prove out the notion that the human lifespan is a mere suggestion. The field has refined its focus from more primitive and heavy-handed methods, such as cryogenically freezing a human head for reattachment to a body sometime in the future, to elegant solutions that take genetics and micro science beyond its post-sci-fi limits. With the acceleration of AI propelling a rumor of human lifespans being doubled within the century, the potential for immortality is closer than ever.
Breakthroughs in medical science that reengineer genes to eliminate chronic and fatal diseases, methods for making your body's processes more efficient, and even uploading your consciousness into computer-based storage are all ideas for immortality that aren't just being floated; they're being actively attempted to bring the notion of immortality into the realm of possibility. Take a look at some of the mind-bending and ingenious paths that science, medicine, and technology are working on to extend good health and human life indefinitely.
Gene editing can provide life-extending advantages
Thanks to a space-age technology called CRISPR, DNA alteration in humans has leapt from the pages of science fiction to the agenda of scientific reality. The term "gene editing" allows bioengineers to do just what it says: edit genes to produce a desired response that either resolves a disease or strengthens your immune system to fight disease more successfully. CRISPR stands for "clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats," a system that scientists first discovered in microbes. It works as an immune defense against viral attacks in microbes like bacteria. The microbes utilized CRISPR to adopt DNA from the virus so it can be recognized down the line and used to prevent subsequent infections — similar to what the human immune system does to establish immunity.
With CRISPR in the immortality toolbox, mutated genes that would otherwise run rampant can be repaired, allowing humans to overcome genetic damage. This can help with diseases that are passed down through generations. The mechanism can also control defective genes to provide resolutions for diseases like cancers, where a patient's own immune response is bolstered by introducing engineered T cells that attack tumor cells more ferociously. Similar targeting can be engaged for other diseases like sickle cell anemia.
Targeted gene therapies may soon cure chronic illnesses
Medical therapies that zero in on offending genes to fix the basic wiring of human physiology are already in play, giving cancer patients a fighting chance at longer lives. Tech monarchs in Silicon Valley are investing heavily in the concept of "super longevity," which makes use of gene therapy to program human DNA to defy aging and cure chronic illnesses that currently require ongoing maintenance without the promise of an ultimate cure. Rather than simply making life last longer, these therapies aim to keep the human body pliable and healthy, reinvigorating systems and ensuring ongoing vitality that makes living longer (or forever) worthwhile.
With the Food and Drug Administration approving gene therapies for several diseases already and clinical trials underway for others, the potential for genetic intervention to reverse and reconfigure abnormalities and reset human physiology will provide extended life for many patients who might not have lived their natural life span otherwise. There are risks however, such as undesirable immune responses, infections, and genetic errors that arise as a result of the therapies. Continued development will hopefully iron out the wrinkles and provide answers that help make targeted gene therapy a staple of life extension in the future.
Creating mRNA vaccines is helping eliminate fatal diseases
One of the biggest breakthroughs in recent medical science is the use of mRNA, or messenger RNA, to develop vaccines for some unexpected conditions. Though this molecule was discovered in the 1960s and scientists began researching its potential in the 1970s, it was the COVID-19 pandemic that stimulated the rapid response by bringing a vaccine to market using mRNA. Though the speed at which a COVID vaccine was achieved using mRNA has caused unending controversy, the results that this technique provide offers a window into what's next for messenger RNA-based serums.
Beyond just providing protection from viral infections, mRNA serums show potential for being a scientific miracle that fights some of the biggest diseases in the world, conditions like pancreatic cancer, and even a universal vaccine that may be able to knock out essentially any cancer when paired with immune checkpoint inhibitors, anticancer drugs that are already commonly used.
"This finding is a proof of concept that these vaccines potentially could be commercialized as universal cancer vaccines to sensitize the immune system against a patient's individual tumor," says Pediatric Oncologist Elias Sayour (via UF Health). A world on the cusp of a cancer vaccine is a world peering across the void of immortality and seeing light on the other side.
Nutritional breakthroughs are helping keep humans alive longer
It's no surprise that nutrition is foundational in the concept of immortality; if you are what you eat, then eating better is bound to equate to living better and longer ... isn't it? There's a slew of dietary information that taps into the thrill of eating for health and achieving longevity through nutritional means. It's often used as an antidote — literally — to the methods offered by the American medical system, and it's one of the simplest tacks to take when doing what you can to give yourself a chance at a long, healthy life.
But while the obvious practices of eating a healthy diet have been touted as a life-extending technique, there's also an element of caloric restriction that's proven successful in extending lifespan. The trick is to avoid malnourishment while using the body's own metabolism to stimulate cell repair and minimize damage. There's also an element of staving off age-related diseases that makes the possibilities even more thrilling. More study is needed to better understand the dynamics and potential outcomes. But the prospect of using nutritional mechanisms to extend life is one of the more exciting and easily engaged possibilities for immortality.
Biohacking is being pioneered to extend lifespans, potentially indefinitely
The word "biohacking" has become a darling term in the world of immortality in recent years, thanks to developments that maximize the body's own mechanisms to minimize and undo damage in the service of life extension. No one embodies the concept of biohacking more completely than billionaire Bryan Johnson, whose efforts to turn back his biological clock include sleep manipulation and transfusions. So far, Johnson has spent $2 million in pursuit of immortality, the results of which have kept him looking fit and youthful in his late 40s, and have hopefully propelled him toward his goal of living until the year 2140 (via The Economic Times).
If the magic of biohacking can truly add years to your life (and life to your years), you have simple processes that you can engage in now that don't take millions of dollars or access to cutting-edge technology. Simple processes like getting adequate sleep, eating a healthy, plant-heavy diet, minimizing stress, and avoiding alcohol are all easy biohacks that, while not as sexy as sleeping in a hyperbaric chamber or having your blood replaced periodically, are easy to incorporate into your daily habits. It's a simple start toward your own personal immortality.
Nanobots are on the cusp of extending human life
Imagine microscopic robots coursing through your bloodstream, racing to regions of your body in need of repair and helping to keep you alive as long as you so desire. Futurist Ray Kurzweil is convinced that nanobots with this sort of purpose are inherent in the concept of human immortality, and he delves deep into it in his book, "The Singularity is Nearer," which details the need for these miniscule machines in ridding the body of cell damage that causes aging, deterioration, and eventually death (via Popular Mechanics). "The only solution, longevity researchers argue, is to cure aging itself," Kurzweil said in an essay written for Wired.
How will such a process work? With guidance from AI, of course, which will not only guide the development of such nanobots but will also provide the superior transhuman intelligence required to put the process into effect. Kurzweil's prediction is that in the 2030s, nanobot maintenance on the human body will bring about a form of immortality that merges man and machine in a truly Twilight Zone-style convergence.
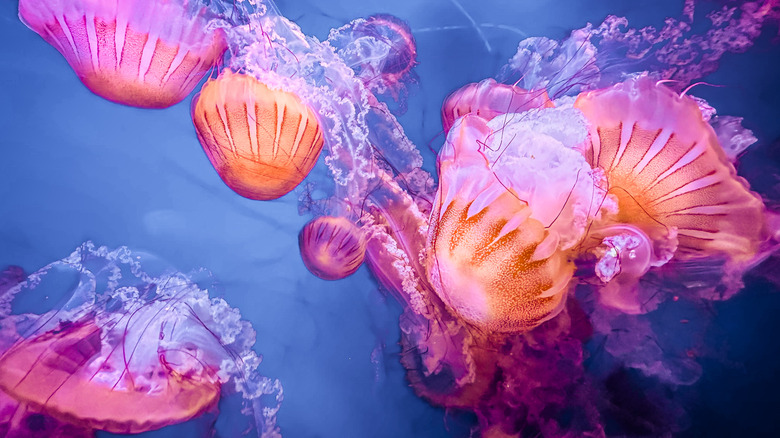
Studying immortal species like jellyfish is helping unlock the secrets of life extension
If there are already species that experience a form of immortality, why not tap into their inner workings to see if we can harness the magic for humanity? Science has turned its microscope toward the world of animals to find out what can be learned about longevity and how that knowledge can be applied to humankind. A specific species of nearly immortal jellyfish, Turritopsis dohrnii, is able to turn back its biological clock to any era of its own lifespan, a handy feature for anyone seeking eternal youth.
If the possibilities of changing death in the future — or even eliminating it entirely — depend on decrypting the DNA of our fellow creatures, how far into the animal kingdom will science need to reach to find the answers? Steven Austad, biology professor at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, studies aging in different animals to unlock the secrets of what makes some species age quicker than others, and what keeps some, like the tiny, aquatic hydra, from aging at all. One of the discoveries Austad has made is that size matters, telling NPR, "If you actually look at a whole bunch of animals, it turns out that smaller ones actually have more heartbeats and use more energy over the course of a lifetime than large ones." This sort of insight has been instrumental in determining how gene manipulation can give humans a similar anti-aging advantage.
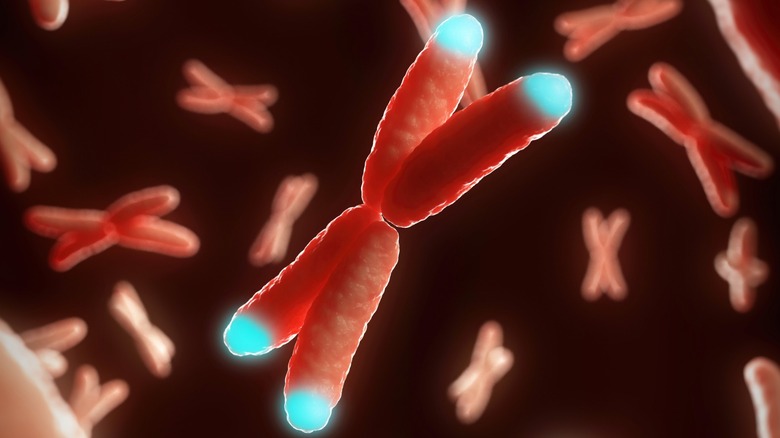
Telomere extension can stave off aging, but there are drawbacks
Telomeres are the caps at the ends of chromosomes that prevent damage to DNA. The extension and preservation of telomeres has been identified as a method for keeping the cellular aging process at bay, a promising direction for the prospect of eternal life that starts at the root of what causes otherwise healthy bodies to break down in the first place. Experiments have proven that telomeres can be manipulated to grow back in cell cultures (via Stanford Medicine), giving hope that someday soon there might be a way to intervene on behalf of longevity. Even more encouraging are discoveries that lifestyle changes like adopting a plant-based diet, reducing stress, and engaging in moderate exercise can help maintain telomeres and give humans a chance at a longer life, per USCF.
But telomere lengthening isn't without its risks, as current science has begun to demonstrate. According to Mary Armanios, M.D., an oncology professor at Johns Hopkins University who conducted a two-year study of telomere length and tumor development, "Cells with very long telomeres accumulate mutations and appear to promote tumors and other types of growths that would otherwise be put in check by normal telomere shortening processes." So while the concept is promising, the reality of telomeres and longevity is complex and requires more examination.
Cryonics is a long-held possibility for humans becoming immortal
You've undoubtedly heard the lore about Walt Disney's head being frozen in a tank, quietly awaiting a future moment of resurrection. The field of cryonics described in this way sounds more like someone's wacky, futuristic Frankenstein fever dream. But the reality is that this form of physical preservation is an industry that's been in motion for quite some time, circling back every so often and entering the conversation on immortality. For those who believe in its potential, it's a concept that holds great promise, though the execution has yet to be proven out in full.
Robert Ettinger launched the cryonics movement in the 1960s, predicated on the basic notion that if you could suspend animation in a human being, you could keep a body in limbo until a future time when fatal conditions could be cured. Then, the body would be reanimated and healed (the process often involves decapitation, like the Disney tale suggests). Though the particulars are much more intricate, as detailed in Ettinger's "The Prospect of Immortality," there are companies like Alcor that employ cryonic technicians and actively offer cryonic suspension for anyone with faith in a forever future somewhere down the line.
3D printing of replacement organs may help humans live indefinitely
What if you could replace your failing organs without requiring a donor transplant? Would you be able to circumvent the eventual deterioration of your own systems with a steady supply of stand-in arteries, livers, and lungs and keep your own mortality at bay? That's the promise at the heart (pun intended) of 3D organ printing technology, a wildly intriguing development that produces the biological hardware required to extend human life into the foreseeable future and beyond by using a patient's own cells taken from small bits of tissue extracted via needle biopsy or a minor surgical procedure. Dr. Anthony Atala, director of Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine, told CNN, "By taking this small piece of tissue, we are able to tease cells apart (and) we grow and expand the cells outside the body." This could reduce the need for donors and reduce the risk of rejection.
Like many immortality efforts, funding will be key with 3D organ printing, and the process may only be available to elite patients. Such a specialized need is bound to come with a high price tag, at least initially, and with advancements in printing human blood vessels that accurately recreate circulatory networks (via Harvard), the specificity of organ printing will undoubtedly be a costly endeavor. But in the pursuit of immortality, is price really an obstacle?
Becoming code through digital immortality could keep humans alive forever in the cloud
Rather than maintaining your current life via a physical existence, there's a very real possibility that soon you'll be able to upload your consciousness to digital storage for a virtual version of immortality that could keep you around without a time limit. It's the subject of tech startup Nectome, a company created by MIT graduates Robert McIntyre and Michael McCanna for the purpose of producing neural mappings that can be stored as cloud-based representations of the human mind. It's the stuff of the most imaginative Black Mirror episodes, but it's closer to becoming a reality every day.
Imagine not needing a body or even a brain to continue living. Someday, your descendants may be able to interact with your computerized avatar, engaging with a version of you that arises through an AI-based collection of your thoughts, memories, and feelings. There are already programs that replicate speech patterns of the deceased, allowing loved ones to "communicate" with the dead, and it appears to be only a matter of time before digitized brainwaves will provide code-based immortality, a phenomenon that's sure to come with a hefty price tag.
Designer babies may be coded for immortality from conception
The concept of the designer baby often centers around choosing physical attributes like eye color, hair color, and height. But babies could also be engineered for longer lifespans. Rather than trying to keep life rolling forward once it's begun, cutting-edge science offers the possibility of creating designer babies with built-in immortality, thanks to customized genetic compositions that let humans sidestep their inevitable decline. Science already has the ability to manufacture chromosomes; composing the genetic structures of children who don't succumb to disease or degeneration is a logical next step.
Of course, the ethical conundrum of genetically engineered embryos is already the subject of conversation among the legal community, as well as the scientific community. In Shenzhen, China, scientist He Jiankui declared that twin embryos edited using CRISPR had resulted in the first genetically engineered babies. Though the goal was to imbue the children with resistance to the HIV virus, which was present in the children's father, the implications sent shockwaves around the world and extended the path toward manufactured immortality by at least a mile or two.